Functional Reactive Programming with Bacon.js
Reaktor Academy 22.4.2015
Olli Mahlamäki / Reaktor
Agenda
- Quick introduction
- Functional Programming
- Functional Reactive Programming
- Workshop
- 5 exercises
- Concrete API tips inbetween
Functional Programming
What is it?
Definition
“In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm, a style of building the structure and elements of computer programs, that treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions and avoids state and mutable data.”http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Functional_programming
Important parts
- Pure functions
- Avoid state
- Immutable data
- Higher order functions
Pure functions
- Depends only on parameters
- No side-effects
Is this pure function?
function sum(x, y) {
return x + y;
}
display(sum(4,8));
Is this pure function?
var n = 7;
function addN(x) {
return x + n;
}
display(addN(4));
Is this pure function?
var i=0;
function count() {
return ++i;
}
display(count());
display(count());
Is this pure function?
function fibonacci(i) {
if(i < 3) return 1;
return fibonacci(i-1) + fibonacci(i-2);
}
display(fibonacci(7));
Is this pure function?
function warn(message) {
window.alert("Warning: " + message);
}
warn("Audience participation needed");
Side-effect examples
- Set global / parent scope variable
- Display something to user
- Read value from user
Side-effects are unavoidable!
The point in functional programming style is to separate them from rest of the code
Discussion:
- What are the benefits of pure functions?
- Examples of side-effects
State
- Makes code harder to understand
- Harder to test
- Often unavoidable, but don't spread it everywhere
State (evil example)
var calculator = new Calculator();
calculator.addInput(5);
calculator.addInput(10);
calculator.sumInputs();
console.log(calculator.getValue());
No state
console.log(Calculator.sum(5,10));
State (slightly less ridiculous case)
var center = new Point(15, 40)
var radius = 15
var circle = new Circle(center, radius)
circle.draw(canvas)
center.setX(30)
circle.draw(canvas)
Discussion
- Can you think of real life examples of bugs resulting from state?
- How would you refactor previous example?
Immutable data
- Copy instead of modifying
- Keeps bugs away
- Immutable data is a great default option, only mutate when there is a real need for it
Example (evil)
function Point(x, y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
Point.prototype.moveBy = function(deltaX, deltaY) {
this.x += deltaX
this.y += deltaY
return this
}
function distanceUntilNegative(point) {
var d = 0;
while(point.x >= 0 && point.y >= 0) {
point.moveBy(-1, -1)
d++
}
return d;
}
var pos = new Point(3,5)
display(distanceUntilNegative(pos))
display(pos)
Example (better)
function point(x, y) {
return { x: x, y: y }
}
function moveBy(p, deltaX, deltaY) {
return point(p.x + deltaX, p.y + deltaY)
}
function distanceUntilNegative(point) {
var d = 0;
while(point.x >= 0 && point.y >= 0) {
point = moveBy(point, -1, -1)
d++
}
return d;
}
var pos = point(3,5)
display(distanceUntilNegative(pos))
display(pos)
Up to the JavaScript programmer
- In LISP, Scala etc., the language encourages immutable data
- Javascript: you can always mutate, but you shouldn't
- Performance: copying is slightly slower, but often it doesn't matter
Tools help
- Immutable.js from Facebook
- Final fields in Java code
Higher order functions
- Functions that take another function as parameter
- Academically interesting and complex
- Really practical in real life
Examples of useful higher order functions
- map
- filter
- reduce
- any
- all
Summary
- Pure functions
- Avoid state
- Immutable data
- Higher order functions
Functional Reactive Programming
Definition
“Functional reactive programming (FRP) is a programming paradigm for reactive programming using the building blocks of functional programming. FRP has been used for programming GUIs, robotics, and music, aiming to simplify these problems by explicitly modeling time.”
Functional Reactive Programming
- Based on functional programming
- Building blocks: Values changing over time
- Calculations done with pure functions
- Concept of current value missing!
Bacon.js
Javascript FRP library
- https://github.com/baconjs/bacon.js
- Made in Reaktor by Juha Paananen
Used in production
Other FRP libraries
- RxJS - javascript library similar to Bacon.js
- Reactive extensions (C#)
- RxJava is popular for building Android apps
- React (js framework by Facebook) is not an FRP library, but it does work great together with Bacon or RxJS
EventStream
- Stream of events with value
- From user input
- From other EventStreams
Exercise 1
- Use .asEventStream to create a stream from click events
- http://tinyurl.com/bacon-exercise-1
Map
var mappedStream = stream.map(f)- Creates new stream "mappedStream"
- Gets a value every time there is a value in stream
- If the value of stream is x, the value of mappedStream is f(x)
- f should be a pure function
- f can be as simple as function() { return true }
Filter
var filteredStream = stream.filter(f)- Creates new stream "filteredStream"
- Every time there is a value x in stream, f(x) gets called
- If the function f returns true, the value goes to filteredStream
- If not, the value is skipped
- f should be a pure function
Exercise 2
- Use .map and .filter
- http://tinyurl.com/bacon-exercise-2
Combinators
merge
Merges events from both streams a and b into the result stream.

Result stream ends when both streams have ended.
onValue
- Add listener to the stream
- This is the place for side effects
myStream.onValue(function(value) {
// Called every time myStream gets a value
$("#result").text(value)
})
Exercise 3
- Use .map and .merge to enable and disable textarea
- http://tinyurl.com/bacon-exercise-3b
combine
Combines the latest values of property a and stream or property b using a given function. In this example, a self-explanatory plus function is used.

First output event is generated when both a and b have produced a value. The combined stream ends when both the inputs have ended or one has ended without having produced a value.
Exercise 4
- Use .combine to calculate sum and product of 2 numbers
- http://tinyurl.com/bacon-exercise-4
flatMap
Creates a new stream for each value in the source stream, using the given function f. Merges the events from all created streams into the result stream.
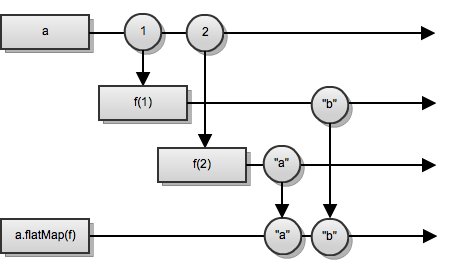
Result stream ends when both the source stream and all the so-far created streams have ended.
flatMapLatest
Like flatMap, flatMapLatest creates new streams for each source event. Instead of merging all created streams, it "switches" (hence the former name "switch") between them so that when a new stream is created, the earlierly created stream is no longer listened to.

Result stream ends when source stream has ended and the latest created stream has ended.
Don't worry
- When you truly understand flatMap & flatMapLatest, everything in Bacon.js becomes simple
- In the next example, you just need to know that flatMapLatest is used when doing ajax requests
Exercise 5
- Use .flatMapLatest to implement image search
- http://tinyurl.com/bacon-exercise-5